Gas prices return to the uptrend and drive European electricity markets prices upwards.
In the second week of August, gas prices resumed the upward trend that stalled at the beginning of the month, reaching on the 15th their highest level since the all?time highs of March. Consequently, prices in most European spot and futures markets were higher than in the first week of August. CO2 prices continued to rise and exceeded €90/t on August 15. Electricity demand decreased in most markets.
Solar photovoltaic and thermoelectric energy production and wind energy production
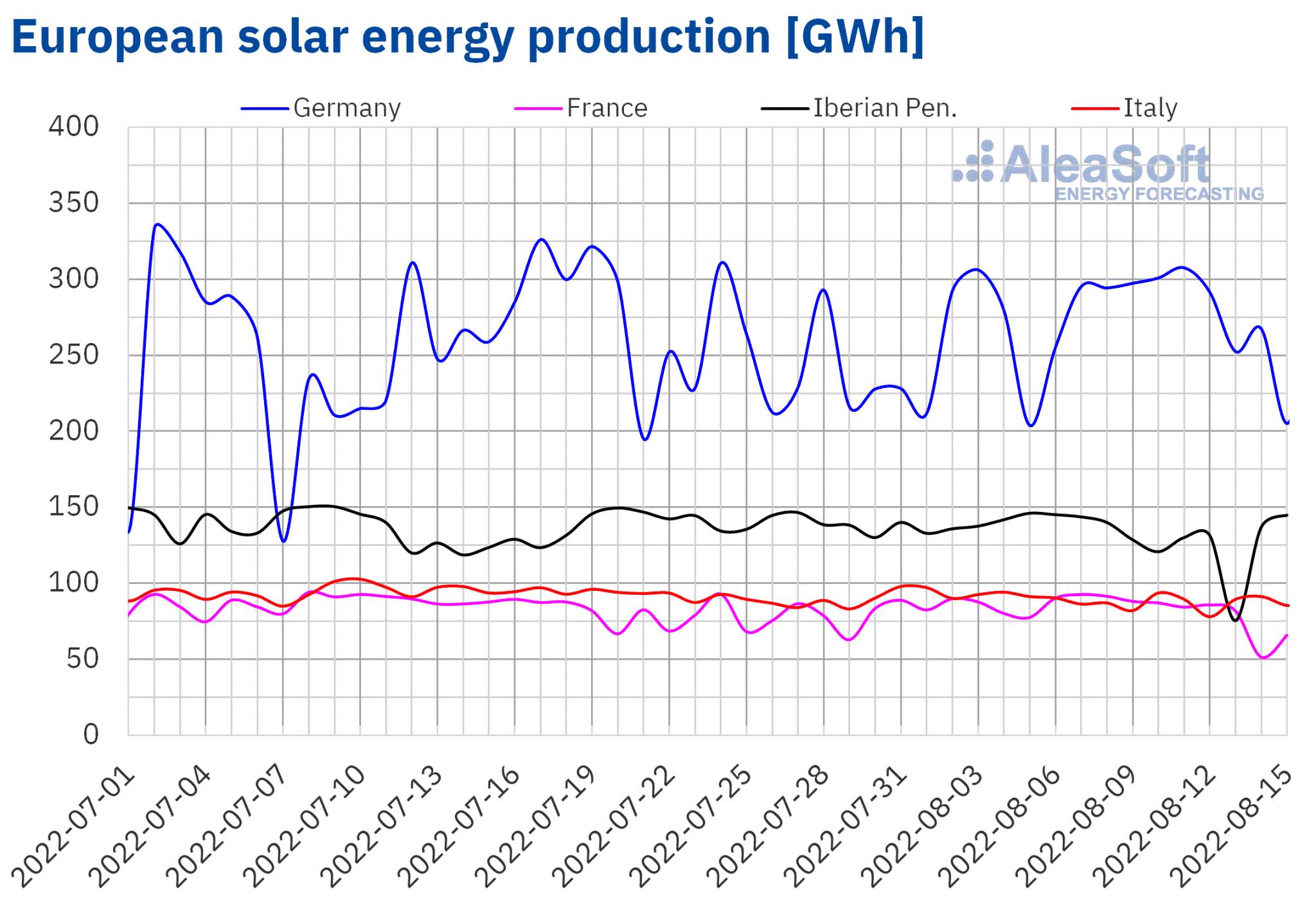
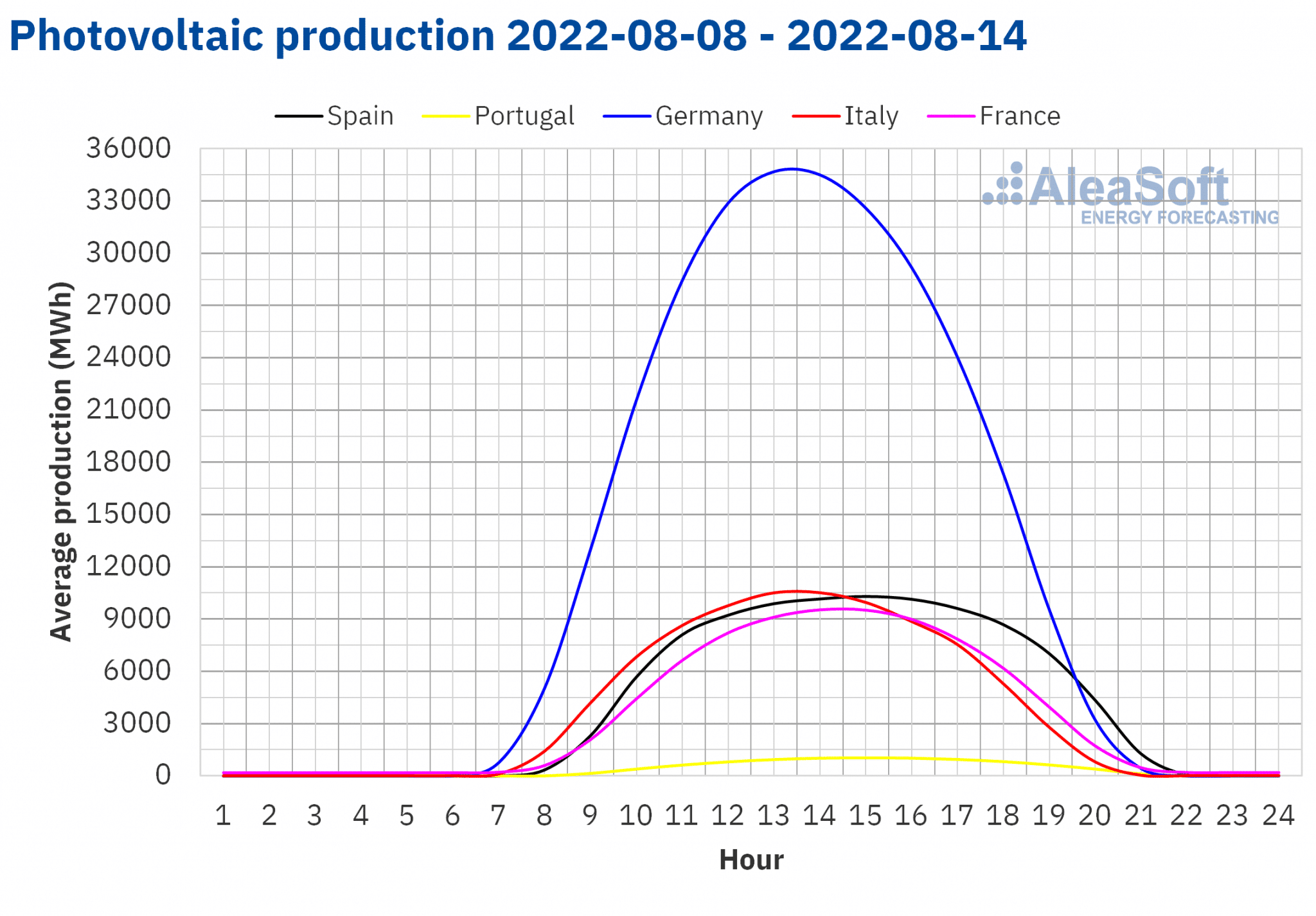
During the second week of August, solar production increased by 9.1% in the German market compared to the previous week. In the other markets analysed at Aleasoft Energy Forecasting, production decreased from 3.6% in the Portuguese market to 13% in the Spanish market.
For the week beginning on August 15, AleaSoft Energy Forecasting‘s solar production forecasts indicate a reduction in production in Germany, Spain and Italy.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
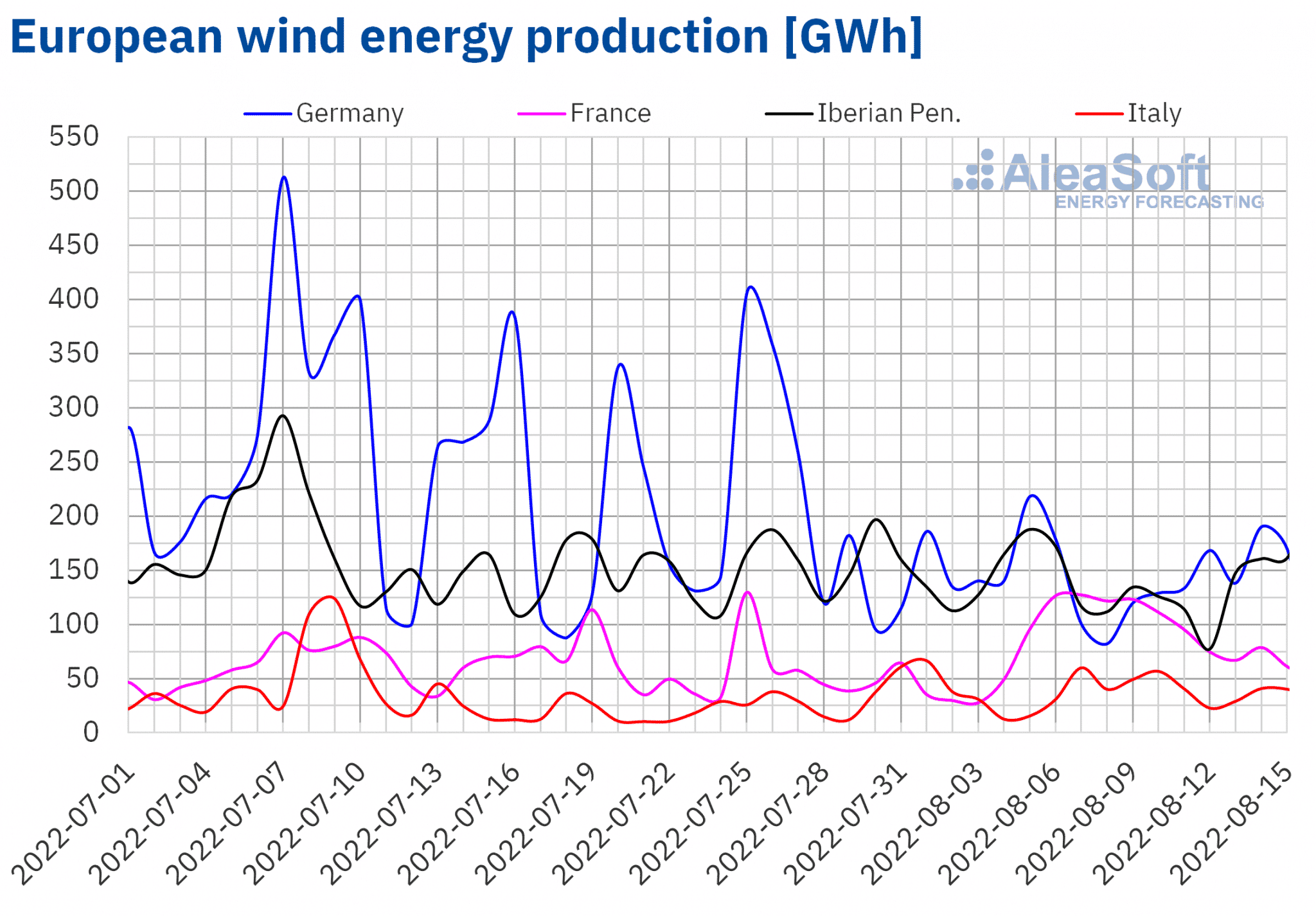
During the week of August 8, wind energy production increased compared to the previous week in the French, Portuguese and Italian markets. In the French market, production increased by 37%, as well as in the Portuguese market, while in the Italian market, production increased by 9.9%. On the other hand, in the Spanish market, production decreased by 19% and in the German market, by 13%.
For the third week of August, AleaSoft Energy Forecasting‘s wind energy production forecasts indicate an increase in the markets analysed, except in the French market, where a reduction in wind energy generation is expected.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
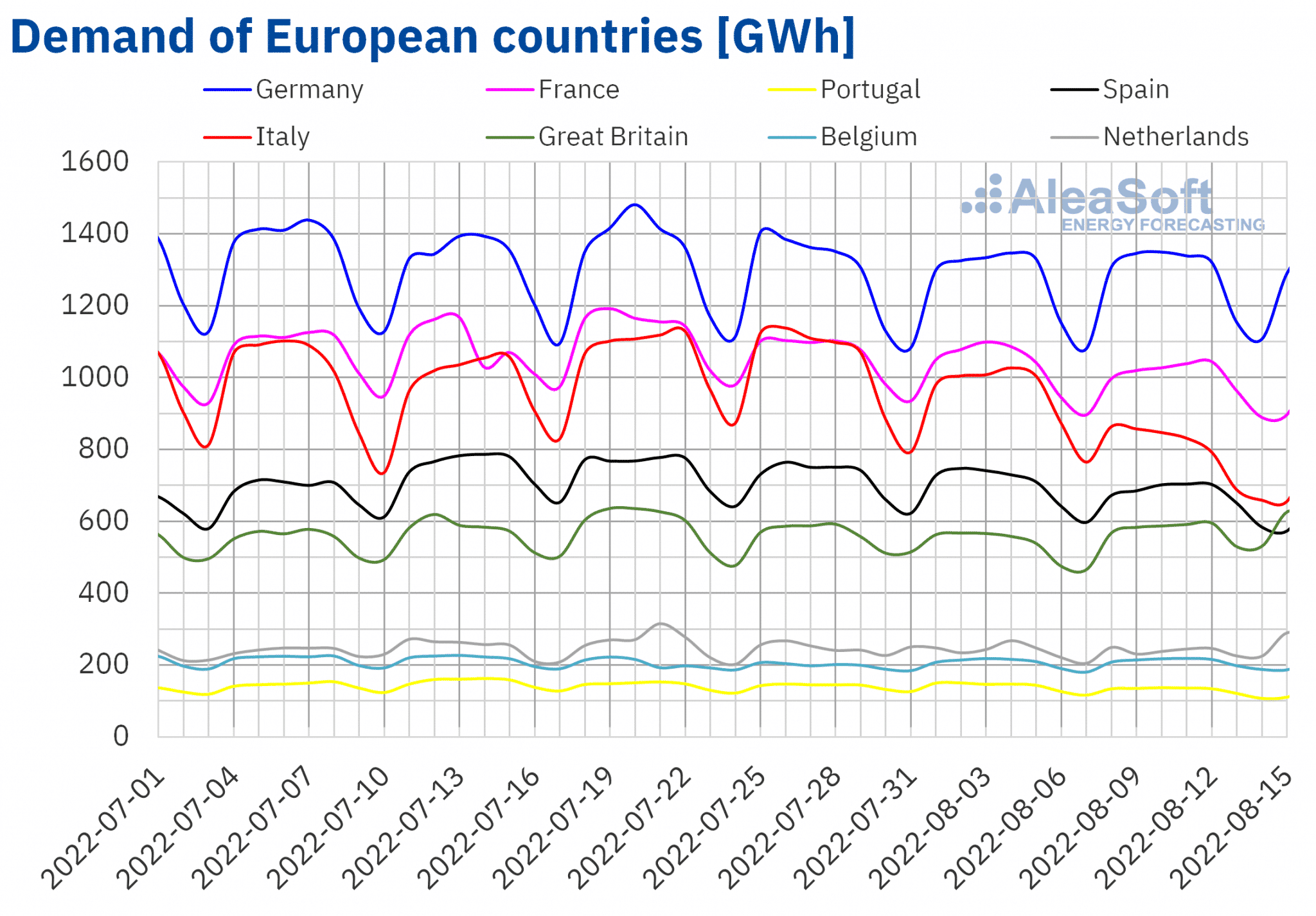
Electricity demand
In the second week of August, electricity demand decreased compared to the previous week in most European markets, mainly due to a decrease in working patterns during the summer holidays. In Italy, a 17% drop was recorded, which was also favoured by a decrease in average temperatures by 2 °C. Demand also fell in Portugal by 7.7%, Spain by 4.0%, France by 3.0% and the Netherlands by 0.4%.
On the other hand, in the UK market, where average temperatures rose by 3.7 °C, demand increased by 6.8%. In Belgium and Germany, demand increased by 1.7% and 0.6% respectively.
On Monday August 15, demand decreased compared to the previous Monday, August 8, in most of the analysed European markets, because of the public holiday of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary, with the largest decrease of 24% in Italy. However, on this day, demand increased compared to the same day the previous week in the markets of Great Britain and the Netherlands, where this holiday is not observed. In these cases, the increase in demand was 16% in the Netherlands and 10% in Great Britain.
According to demand forecasts by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, for the week of August 15 as a whole, electricity demand will fall in Spain, France and Belgium, while it is expected to increase in the rest of the analysed markets.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE, TERNA, National Grid and ELIA.
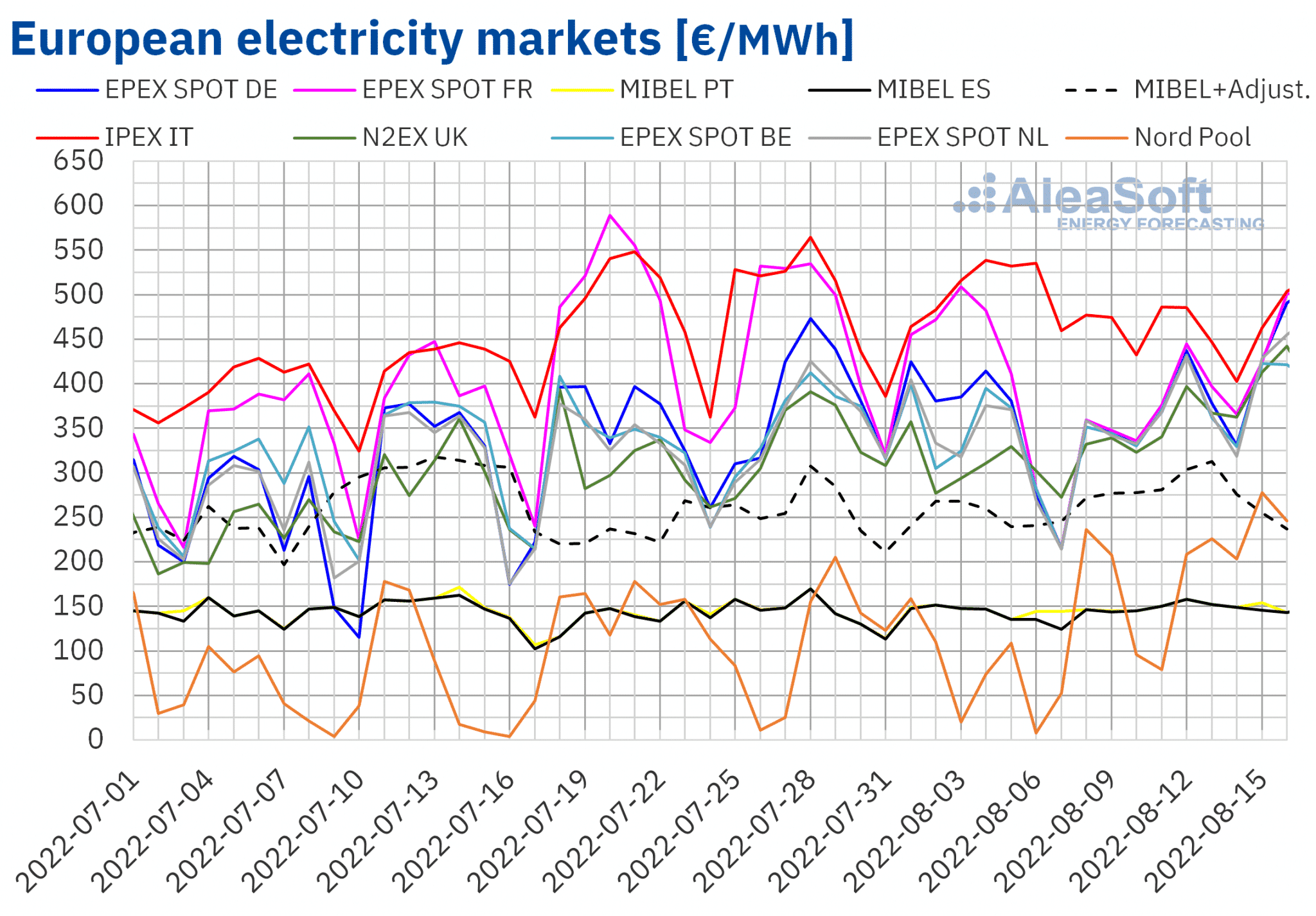
European electricity markets
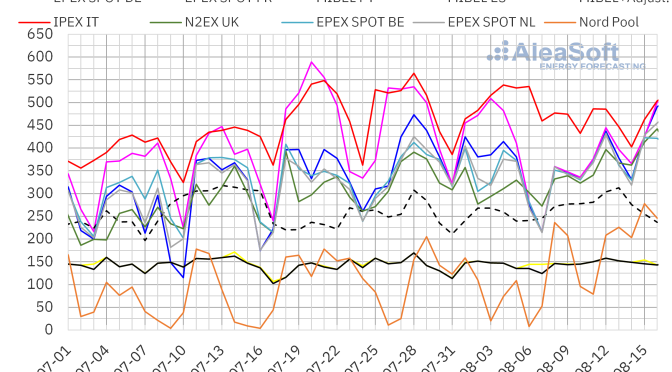
The general price trend in the wholesale electricity markets during the second week of August was upwards, led by the Nord Pool market in the Nordic countries, which rose by 136%, a very pronounced rise from very low prices during the first week of August. Rises in the other countries ranged from 15% in the British N2EX market to 2.6% in the Portuguese MIBEL market. The only two markets where prices fell were Italy’s IPEX and France’s EPEX SPOT markets, which were the markets with the highest prices in the previous week, the first week of August.
Weekly average prices in the week of August 8 were around €365/MWh in the EPEX SPOT markets in the centre of the continent and in the UK market. The Italian market had the highest prices, with an average of €457.91/MWh, and the Nordic market, with €179.48/MWh, had the lowest prices.
The Iberian market averaged just over €149/MWh during the week. The adjustment price to be paid by consumers with market?indexed prices amounted to €136.36/MWh, bringing the total price to €285.63/MWh. Even with the extra cost of the adjustment mechanism, the Iberian price was the second lowest of the analysed markets, only above the Nordic market.
The significant drop in demand in Italy favoured lower prices in that market and, in general, the reduction of renewable generation supported the price increase.
In terms of hourly prices, the lowest prices were recorded on the afternoon of Sunday August 14, when the Dutch market recorded a negative price of €?20/MWh between 13:00 and 14:00. Peak prices remained below €600/MWh, only surpassed during some hours in the afternoon of August 8 on the Italian market.
In the current week of August 15, prices are showing a strong overall upward trend, with the Italian and French markets already back above the €500/MWh daily average on Tuesday 16.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from OMIE, EPEX SPOT, Nord Pool and GME.
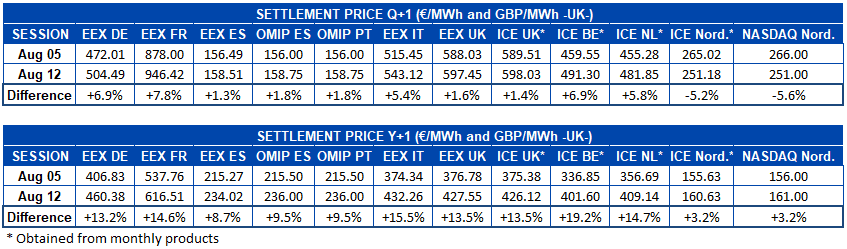
Electricity futures
Electricity futures prices for the last quarter of the year increased in most of the markets analysed at AleaSoft Energy Forecasting. A comparison of the settlement prices for the sessions of August 5 and 12 shows that the market with the highest increase was the EEX market in France with 7.8%. It was followed by the EEX market in Germany and the ICE market in Belgium, both with a 6.9% increase. On the other hand, the Nordic region saw a downward shift, with declines of 5.2% and 5.6% in the ICE market and the NASDAQ market, respectively.
Particularly noteworthy was the price reached by the French EEX market, which in the session of Monday August 15 had a settlement price of €975.55/MWh, very close to breaking the €1000/MWh barrier.
As for electricity futures for next year, the behaviour in the analysed period was of increases in all markets. In this product, the Belgian ICE market led the increases with a rise of 19%. At the other extreme there was again the Nordic region, which, in both the ICE and NASDAQ markets, had an increase of 3.2%.
In the analysed products, both Q4?22 and Cal23, the increases in the OMIP market in Spain and Portugal, and in the EEX market in Spain, are appreciably lower than in the rest of the markets in the region. One of the main causes of this behaviour is the application of the gas price cap until May 31, 2023, as gas is precisely one of the main drivers of price increases.
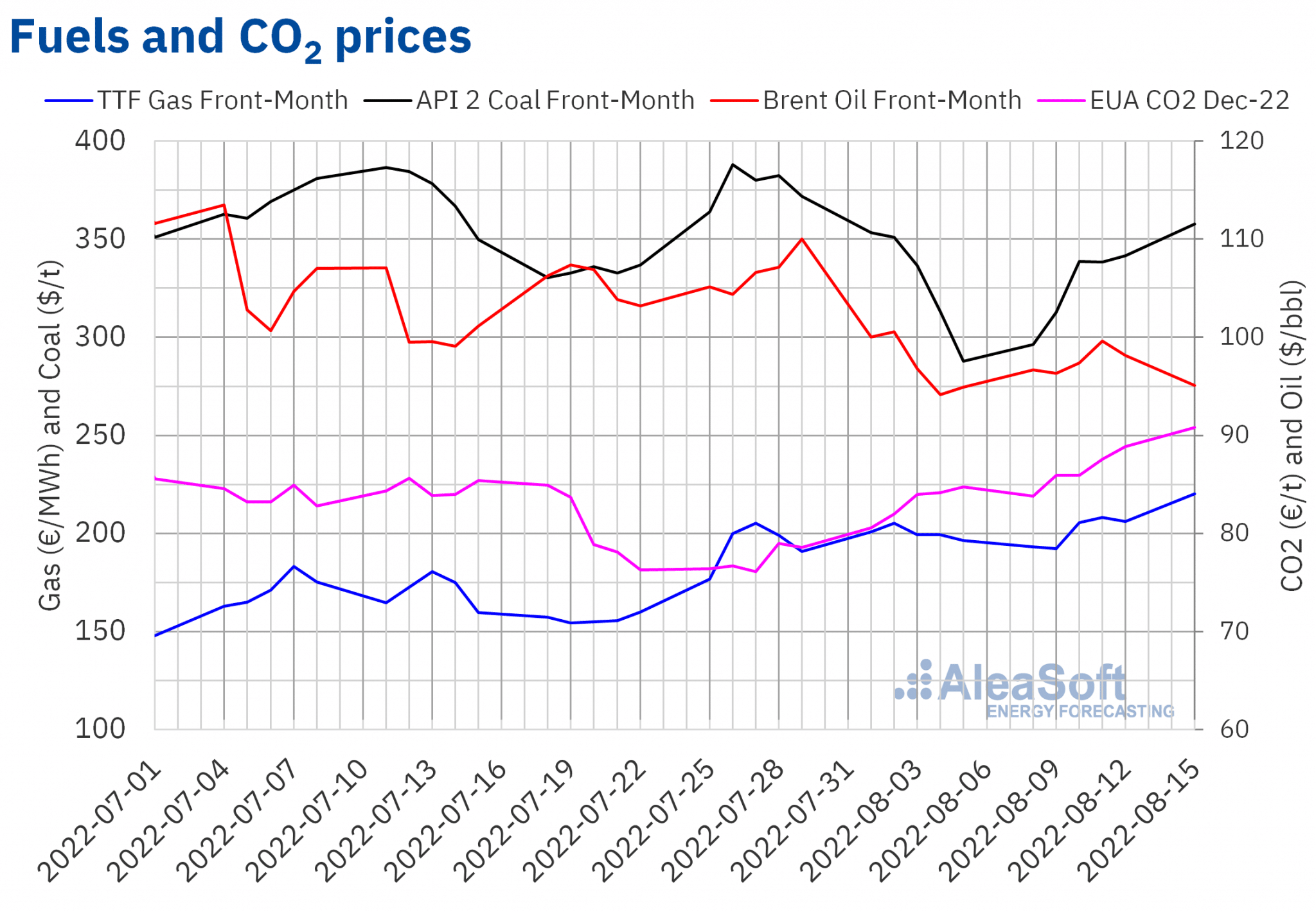
Brent, fuels and CO2
Front?Month Brent crude oil futures have remained below $100 per barrel throughout the second week of August, and on Monday 15 they were as low as $95.10, at the level of prices at the end of the first week of the month. Such a low?price level had not been reached since mid?February.
Concerns persist about a possible global recession and the impact it would have on oil demand, while supply remains healthy.
The opposite is true for TTF gas futures, whose Front?Month prices reached €220.11/MWh on Monday August 15 at their settlement price, the highest value since the historical records of March, at the beginning of the war in Ukraine. During the second week of August, the price trend was upward after the previous week’s decline.
The high gas demand in Europe to maximise storage in preparation for a critical winter situation is driving this sharp rise in prices, together with fears of further reductions in gas flows from Russia. This situation is compounded by maintenance work on the Norwegian continental shelf.
On the other hand, CO2 emission allowance futures prices for December 2022 continue the bullish run they started at the end of July, taking prices per tonne from €76 to over €90 on Monday August 15. Even so, prices remain for the moment below €92, which is the highest price reached since the sharp fall in prices at the end of February, at the start of the war in Ukraine.
The low volume of allowances auctioned in August, together with an expectation of high thermal production, due to the general situation of drought and low hydroelectric production, is encouraging the price rise. In addition, the low market liquidity in August favours more volatile price behaviour.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ICE and EEX.
AleaSoft Energy Forecasting’s analysis on the prospects for energy markets in Europe and the renewable energy projects financing
The next two editions of the AleaSoft Energy Forecasting and AleaGreen monthly webinars are being organised for September and October. The September webinar will be the 25th edition and will be held on the 15th. On this occasion, Jorge Simão, COO at OMIP, and Pablo Villaplana, COO at OMIClear, will be participating and will analyse the importance of forward markets and hedging for the development of renewable energies. Fernando Soto, General Manager of AEGE, will also participate in the subsequent analysis round table, moderated by Antonio Delgado Rigal, CEO of AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, to inform and resolve doubts about the auction of renewable PPA with electro?intensives consumers. In addition, as usual, Oriol Saltó i Bauzà, Associate Partner at AleaGreen, will analyse the evolution and perspectives of the energy markets.
Registration is also open for the October edition, the 26th, which will take place on the 20th of that month. This edition will feature guest speakers from Deloitte who will analyse the critical situation in which the markets will be facing in terms of gas supply and what the outlook will be for the entire winter.
For past editions of the monthly webinars, recordings can be requested on the AleaSoft Energy Forecasting website. The last edition was the webinar on June 14, with the participation of H2B2 guest speakers Africa Castro, Business Development, and Anselmo Andrade, Integrated Product Director. On that occasion, the topic to be discussed on the future vision of energy in Europe was green hydrogen as a strategic vector in the energy transition. The participants showed how electrolyser projects for hydrogen production can be individually adapted to the particular characteristics of each purpose, e.g. to produce hydrogen with surplus energy from a photovoltaic or wind power plant, to produce hydrogen for the transport sector or for industry using energy from the grid, or for seasonal energy storage. They also highlighted the need for support and clear and stable regulation for the development of renewable hydrogen.