European electricity market prices resist rising gas and CO2 prices thanks to renewable energy.
In the third week of March, European electricity market prices remained at similar levels to those of previous weeks. In most of them, the weekly average decreased compared to the previous week due to low prices registered at the end of the week as a result of high wind energy production and lower demand on those days. Solar energy production increased in most markets, reaching the all?time record of daily photovoltaic energy production for a March month in France and Italy. Gas and CO2 prices increased.
Solar photovoltaic, solar thermoelectric and wind energy production
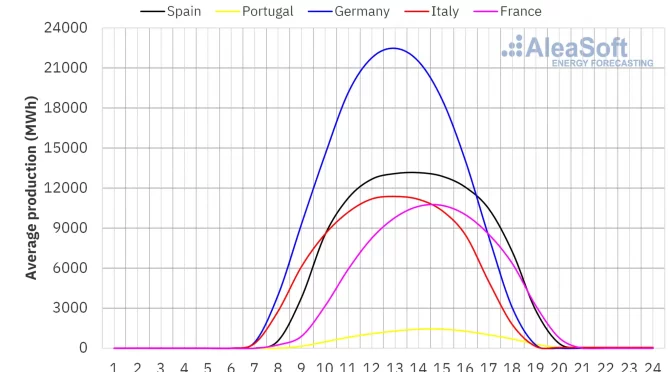
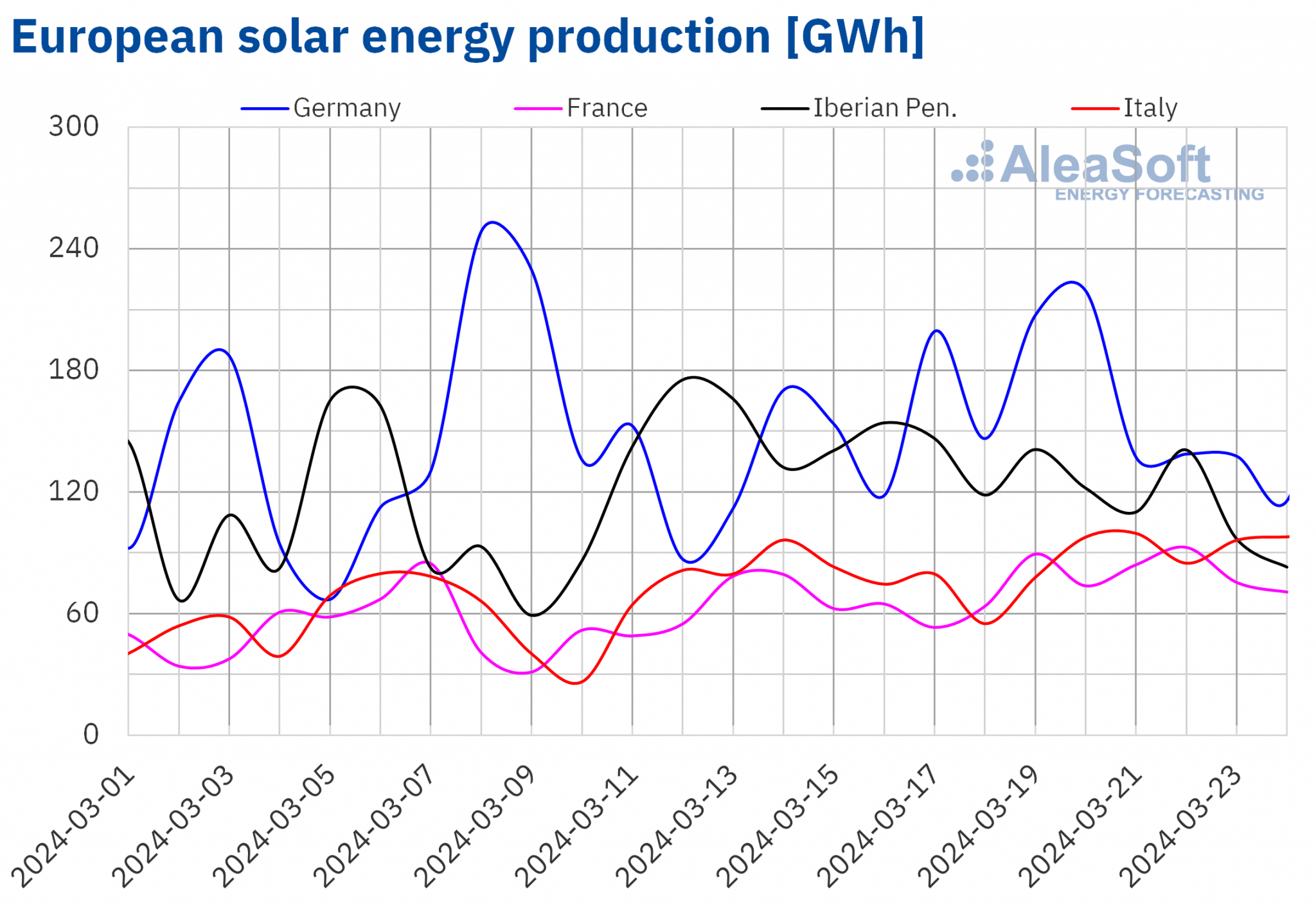
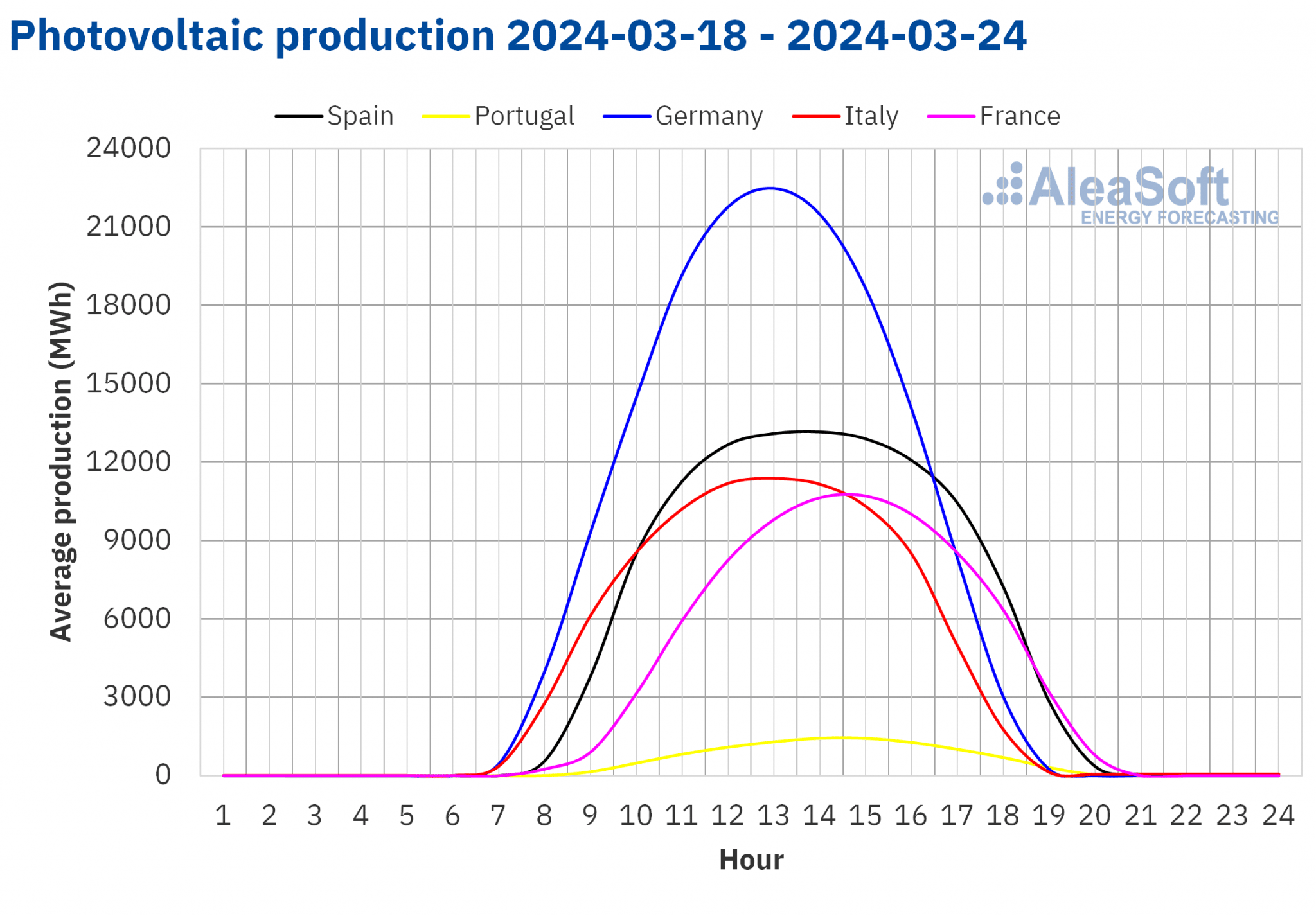
In the week of March 18, solar energy production increased in most major European electricity markets compared to the previous week. The French market registered the largest increase, 24%, maintaining the upward trend for the fourth consecutive week. The Italian market registered the smallest increase, 9.0%, continuing its upward trend for the third week. These two markets registered the highest levels of daily solar photovoltaic energy production for a March month ever. On March 21, the Italian market produced 99 GWh and one day later the French market generated 93 GWh. Both markets last reached these production levels in the first half of September. In the German market, solar energy production also rose, in this case by 11%.
In the Iberian Peninsula, however, solar energy production fell by 23%, reversing the upward trend of the previous week.
For the week of March 25, according to AleaSoft Energy Forecasting’s solar energy production forecasts, the upward trend will continue in the German market. In Spain and Italy, solar energy production will fall.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
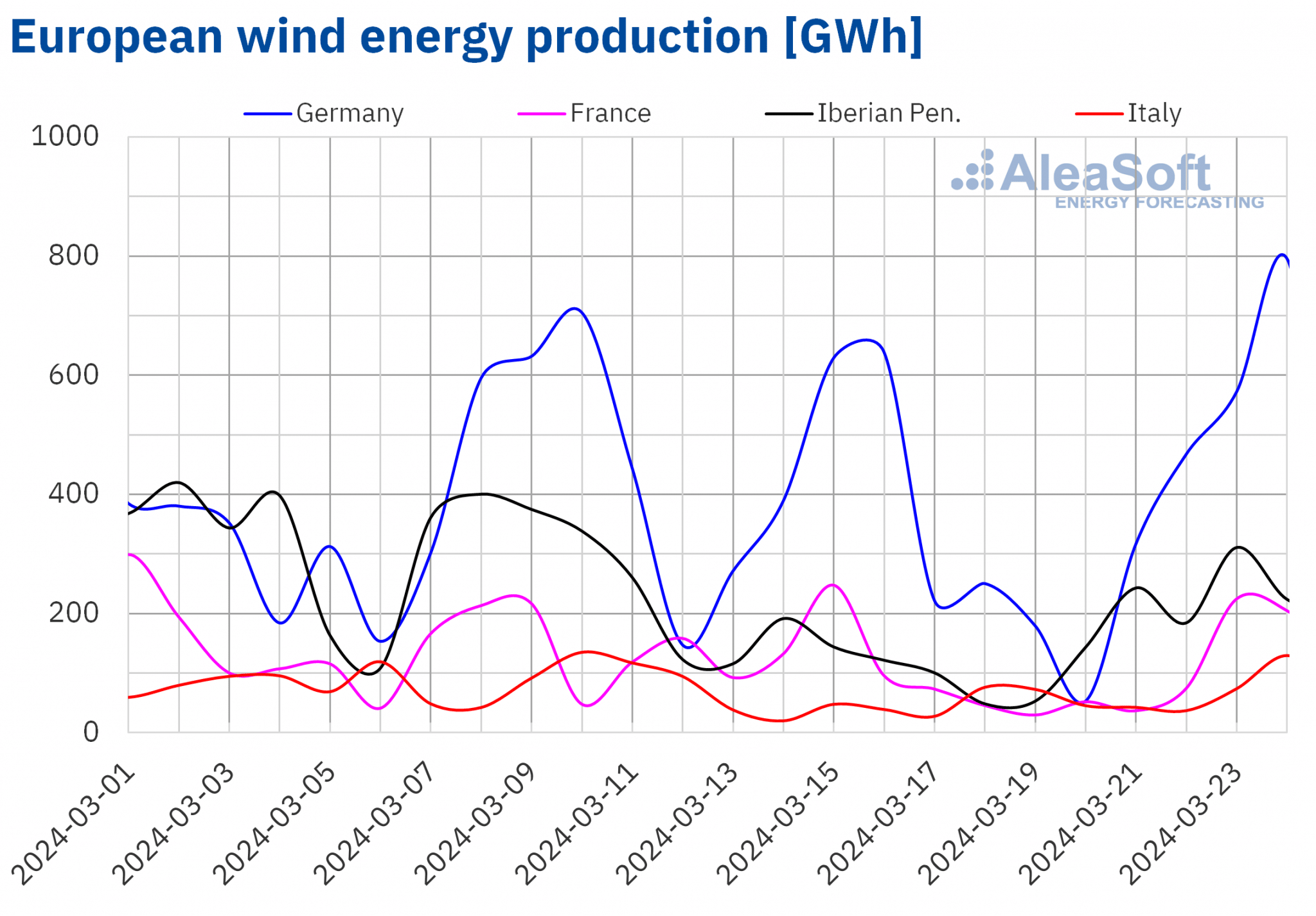
In the week of March 18, wind energy production increased in most major European markets compared to the previous week, reversing the downward trend of the previous week. Increases ranged from 14% in the Iberian market to 24% in the Italian market. In contrast, in the French and German markets, wind energy generation fell by 27% and 3.9%, respectively.
Despite the weekly decline, the German market generated 796 GWh of wind energy on Sunday, March 24, the highest daily value in the last four weeks.
During the week of March 25, according to AleaSoft Energy Forecasting’s wind energy production forecasts, production using this technology will continue the upward trend with increases in Spain, Portugal, Italy and France. In Germany, however, wind energy production will decline.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE and TERNA.
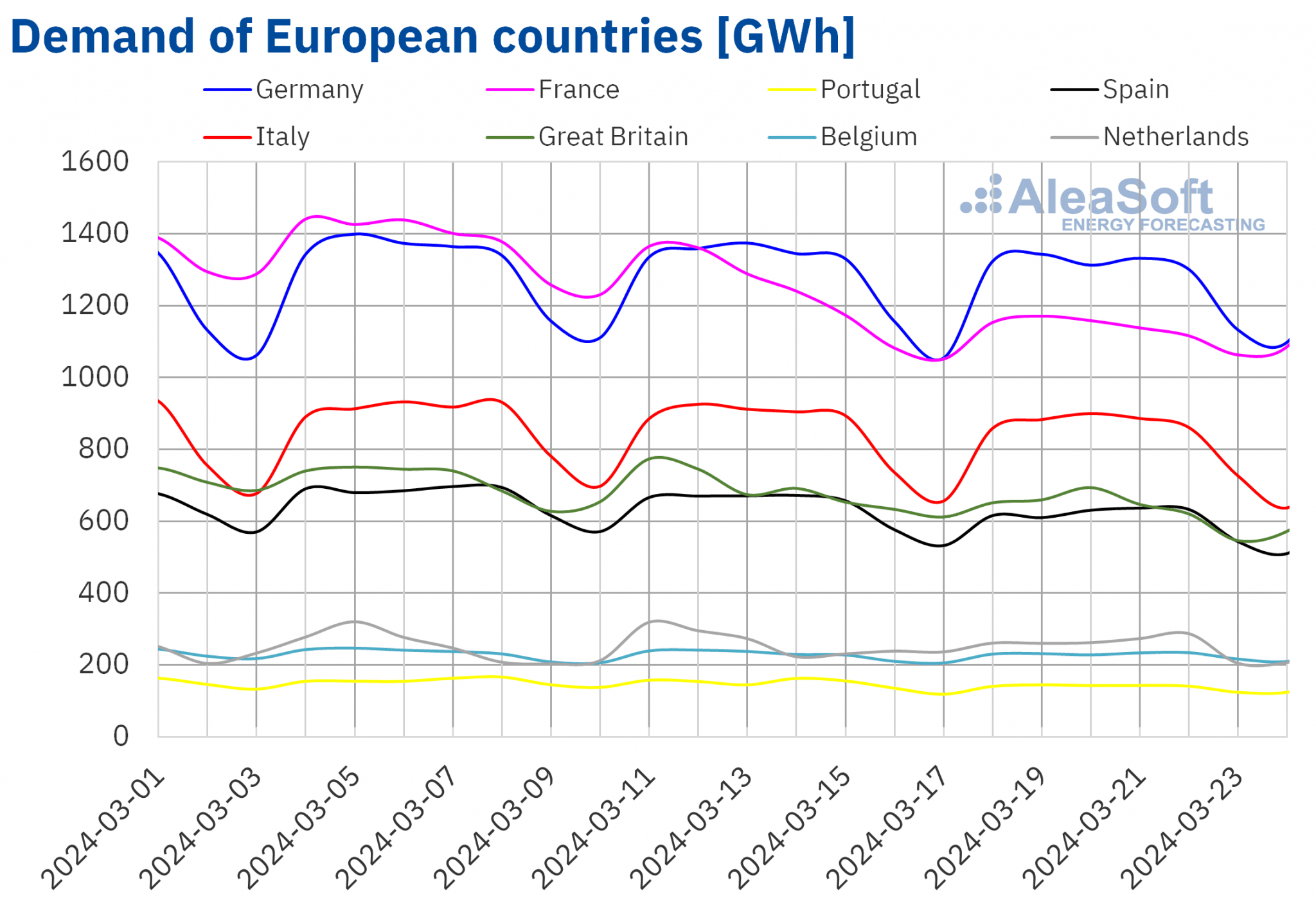
Electricity demand
In the week of March 18, electricity demand fell in all major European electricity markets on a week?on?week basis, continuing the downward trend of previous weeks. The Great Britain market registered the largest decline, 8.2%, and the Belgian market the smallest, 0.4%. In both cases, this was the third consecutive week of declines. In Germany and the Iberian Peninsula, demand fell for the fourth and second consecutive week, respectively. In the case of the Dutch market, the upward trend registered the previous week reversed in the week of March 18.
During the third week of March, average temperatures increased in Southern Europe and France, between 1.0 °C and 2.6 °C. In the rest of the markets, average temperatures decreased between 0.7 °C in Germany and 0.1 °C in Belgium.
For the week of March 25, according to AleaSoft Energy Forecasting’s demand forecasts, the downward trend will continue in Germany, Spain, Italy and the Netherlands. In contrast, demand will increase in France, Portugal, Great Britain and Belgium.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ENTSO-E, RTE, REN, REE, TERNA, National Grid and ELIA.
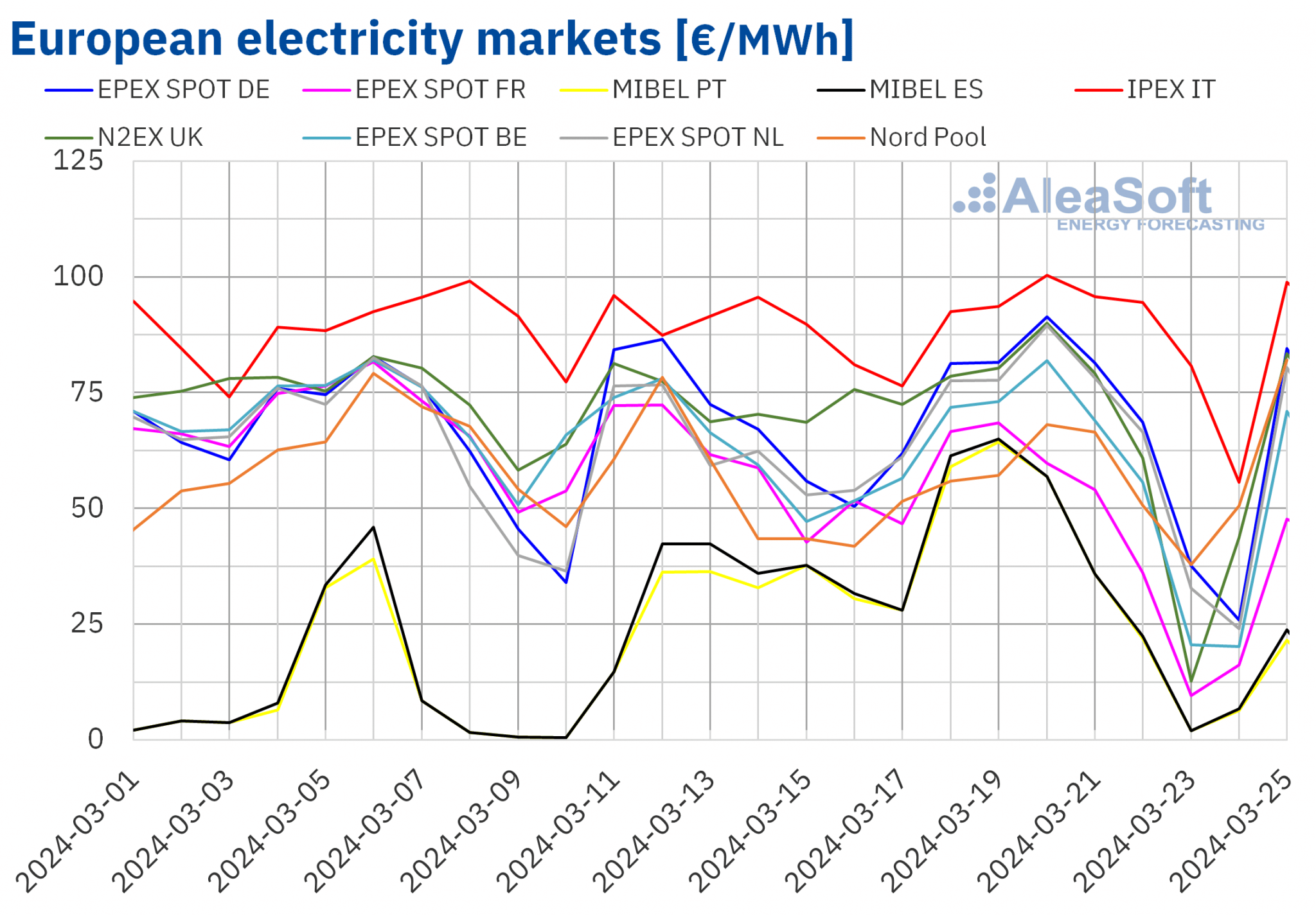
European electricity markets
Between Monday and Wednesday of the third week of March, prices in the main European electricity markets increased, although they remained at levels similar to those of recent weeks. During the second half of the week, prices decreased under the influence of increased wind energy production and lower demand over the weekend. As a result, weekly averages fell in most markets compared to the previous week. However, in the EPEX SPOT market of the Netherlands, the Nord Pool market of the Nordic countries and the MIBEL market of Spain and Portugal, average prices increased by 0.8%, 1.8%, 7.6% and 14%, respectively. In the rest of the markets analyzed at AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, prices decreased between 0.7% in the IPEX market of Italy and 24% in the EPEX SPOT market of France.
In the week of March 18, weekly averages remained below €65/MWh in most analyzed European electricity markets. The exceptions were the German and Italian markets, with averages of €66.79/MWh and €87.59/MWh, respectively. In contrast, the Portuguese and Spanish markets registered the lowest weekly averages, for the seventh consecutive week, €35.20/MWh and €35.76/MWh, respectively. In the rest of analyzed markets, prices ranged from €44.37/MWh in the French market to €63.74/MWh in the Dutch market.
As for hourly prices, on Saturday, March 23, the German, Belgian, British, French and Dutch markets registered negative prices. The latter market reached the lowest price, ?€10.00/MWh, from 13:00 to 14:00. On Sunday, March 24, there were no negative prices, but these markets registered hourly prices of €0/MWh. The Iberian market also registered prices of €0/MWh during 22 hours on March 23 and 24.
During the week of March 18, the general decline in electricity demand exerted its downward influence on European electricity market prices. In the case of Italy, the increase in wind energy production also helped to lower prices. In addition, solar energy production increased in most analyzed markets. However, in the MIBEL market, production using this technology decreased, contributing to the price increase in this market.
AleaSoft Energy Forecasting’s price forecasts indicate that in the fourth week of March prices might decrease in most analyzed European electricity markets, influenced by increased wind energy production in most markets and lower demand in some cases.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from OMIE, EPEX SPOT, Nord Pool and GME.
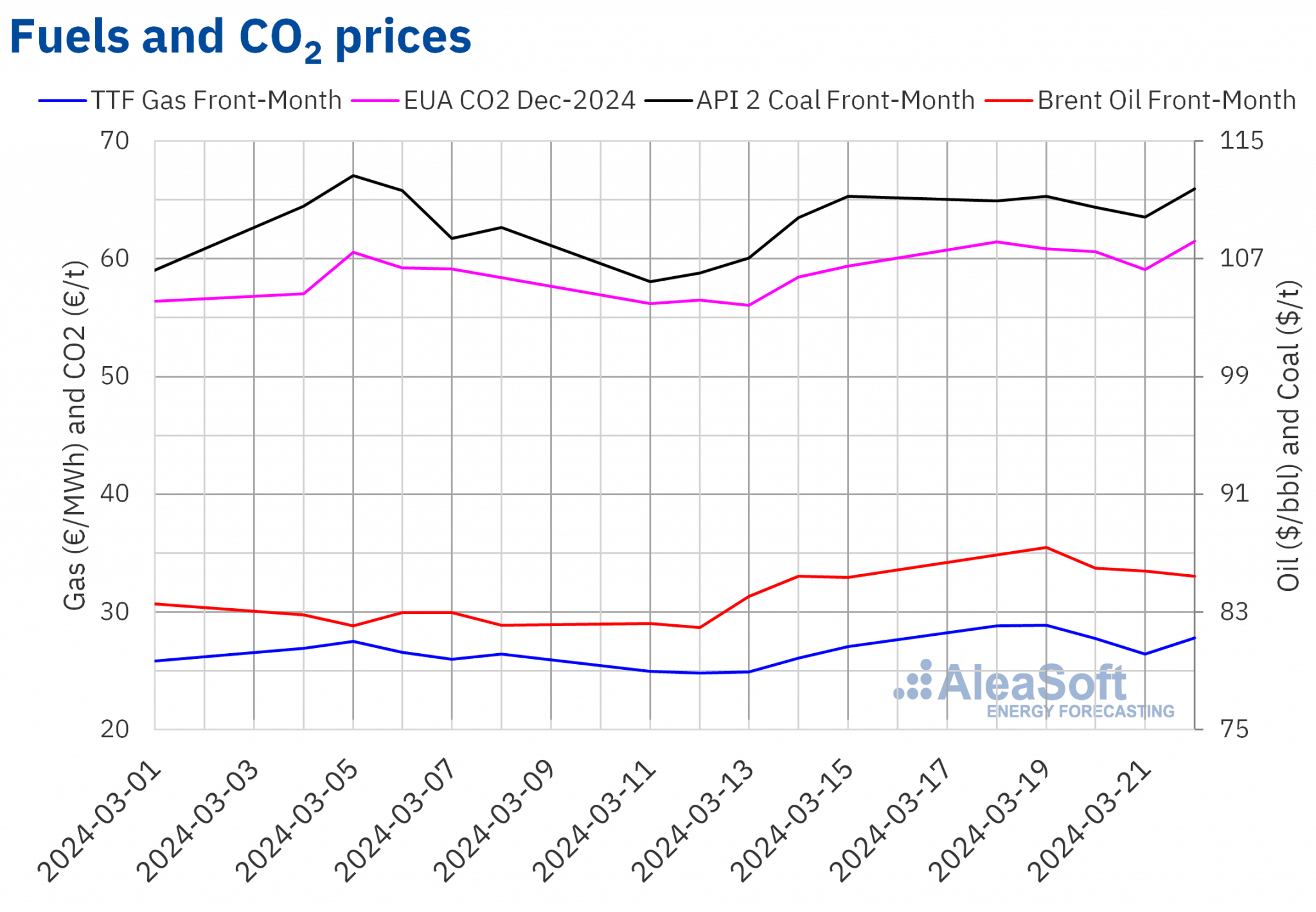
Brent, fuels and CO2
Settlement prices of Brent oil futures for the Front?Month in the ICE market increased in the first two sessions of the third week of March. On Tuesday 19, they reached the weekly maximum settlement price, $87.38/bbl. According to data analyzed at AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, this price was 6.7% higher than the previous Tuesday and the highest since late October 2023. As of Wednesday, prices declined. As a result, these futures reached their weekly minimum settlement price, $85.43/bbl, on Friday, March 22. This price was only 0.1% higher than the previous Friday.
OPEC+ production cuts, as well as attacks on Russian refineries, contributed to the increase in Brent oil futures prices in the first sessions of the third week of March. However, the Middle East peace negotiations and the decision to maintain interest rates in the United States exerted their downward influence on prices in the last sessions of the week. The possibility of price cuts in Russian oil also contributed to price declines.
As for TTF gas futures in the ICE market for the Front?Month, in the third week of March they continued the upward trend of the previous week to reach the weekly maximum settlement price, €28.87/MWh, on Tuesday, March 19. According to data analyzed at AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, this price was 17% higher than the previous Tuesday and the highest since early February. In contrast, these futures registered their weekly minimum settlement price, €26.40/MWh, on Thursday, March 21. This settlement price was still 1.4% higher than the previous Thursday. In the last session of the week, the settlement price increased by 5.2% from the previous day to €27.78/MWh.
In the third week of March, supply concerns continued to drive up prices, which remained limited by the high levels of European reserves. However, the attack on a Ukrainian gas storage infrastructure over the weekend might exert its upward influence on prices in the coming days, as several European countries store gas in Ukraine.
As for settlement prices of CO2 emission rights futures in the EEX market for the reference contract of December 2024, during the third week of March, they remained above €60/t in almost all sessions. The exception was Thursday, March 21. On that day, these futures registered their weekly minimum settlement price, €59.07/t. On the other hand, on Friday, March 22, they registered the weekly maximum settlement price, €61.51/t. According to data analyzed at AleaSoft Energy Forecasting, this price was 3.6% higher than the previous Friday and the highest since the first half of February.
Source: Prepared by AleaSoft Energy Forecasting using data from ICE and EEX.
AleaSoft Energy Forecasting’s analysis on the prospects for energy markets in Europe and the renewable energy projects financing
Coherent and quality long?term price curve forecasts are essential for renewable energy developers. After the gas price crisis, current electricity market prices may affect those developers who used overly optimistic forecasts to get better financing conditions. In early April, AleaSoft Energy Forecasting and AleaGreen will update long?term price forecasts taking into account market evolution during the first three months of the year.
On Thursday, April 11, AleaSoft Energy Forecasting and AleaGreen will hold the 43rd webinar in their monthly webinar series and the fourth in 2024, the year of the 25th anniversary of the foundation of AleaSoft Energy Forecasting. On this occasion, the guest speaker will be Raúl García Posada, Director at ASEALEN, the Spanish Energy Storage Association, who will participate for the third time in the monthly webinars. The April 2024 webinar will analyze the regulation, the current situation and the prospects for energy storage for the coming months.