Electric vehicles provide an important end-use for renewable energy by allowing for the replacement of fossil fuels in certain transport applications. As the market share of EVs grows, they also support the integration of VRE by presenting options for demand-side response, for example through vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology.

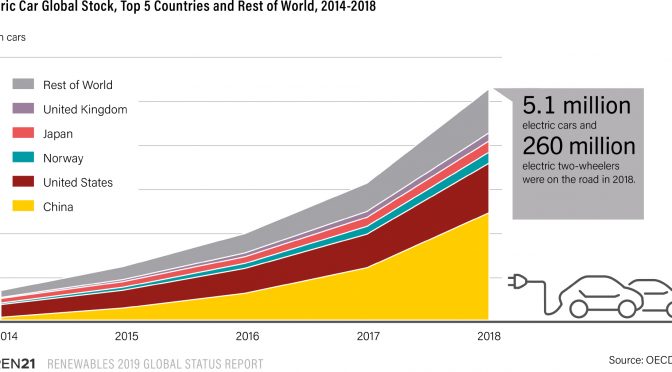
The global stock of passenger EVs (electric cars) reached over 5.1 million units in 2018 – a 63% increase from 2017. Around 2 million new electric cars were sold during 2018, a sales increase of 68% from the previous year. Nonetheless, electric cars still represented a small share of all passenger vehicles, at just over 2.1% by year’s end.
EV markets also remain highly concentrated: as of late 2018, 40% of all EVs in use were clustered in just 20 cities that together account for 3% of the global population.
China had nearly 50% of the global EV stock by the end of 2018, followed by the United States at 22%.
Sales of new EVs reached nearly 1.3 million units in China, including just over 1 million passenger EVs, sales of which increased more than 80% year on year.
Norway remained the leader in the total market share of new electric cars, and around half of new cars registered in the country in 2018 were either battery electric vehicles (BEVs) (30%) or plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) (20%).
The next-largest markets were Iceland at 19%, Sweden at 8% and the Netherlands at 7%.
The
global stock of electric two-wheelers reached around 260 million in
2018, one-quarter of which are in China.103 By one estimate, China’s
electric two-wheelers account for 80% of the avoided greenhouse gas
emissions resulting from the use of EVs.Some 40 million electric
three-wheelers were in use by the end of 2018, virtually all in China.
The
stock of electric buses (both BEV and PHEV) grew more than 25% to about
460,000 in 2018, with the vast majority in China (around 421,000 units)
and slightly more than 2,100 in use in Europe, Japan and the United
States.
Electric
trucks are used mainly in public and commercial fleets in urban
settings. In 2018, waste companies in Brazil and China placed large
orders for electric refuse trucks (200 and 500 units, respectively).
More
than 100,000 public EV charging points were installed in 2018, bringing
the global total to some 395,000 slowcharging units and 145,000
fast-charging units. China was home to more than half (51%) of all
public charging points globally by the end of 2018, followed by the
United States (10%), the Netherlands (7%), Japan (6%) and France/Germany
(5% each).
By early 2019, the United States and Canada together had more than 5,000 fast-charging
points.
Electric Vehicle Industry
The leading manufacturers of passenger EVs in 2018 were (in order of production volume) Tesla, BYD, BAIC, SAIC, Nissan, BMW, Volkswagen, General Motors, Toyota and Mitsubishi.
By August 2018, some 47 plants in China were either manufacturing or planning to manufacture EVs, compared with some 39 plants in the rest of the world.
Chinese
battery manufacturing for EVs also is scaling rapidly. Established
manufacturers of internal combustion engine vehicles – including VW,
Daimler, Nissan, Volvo and others – have made aggressive plans to
electrify their vehicles over the coming decade.
In 2018, the
specific use of VRE to charge EVs was piloted in a one-week US-based
trial by automaker BMW and the California utility Pacific Gas and
Electric (PG&E), during which participating electric cars received
up to 80% of their energy from renewable resources.
To
increase vehicle charging during peak solar production hours, PG&E
sent renewable energy production forecasts to BMW, which then used
incentives and messaging to encourage EV owners to charge their cars at
these times.
The initiative was one of several activities in 2018
aimed at supporting power system flexibility through both the management
of charging times and the implementation of bi-directional charging and
discharging of EV batteries (V2G).
Bi-directional charging could allow fleets of EVs to act as virtual utility storage, enabling higher penetration of VRE.
A
number of V2G-enabled vehicles were available in 2018, and automaker
Honda invested in bi-directional charging at its European R&D site.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers, a global
industry association, is developing technical standards for
bi-directional charging systems; however, wider commercialisation of the
V2G market has been slow.
Considerable efforts to expand EV charging
infrastructure were under way in 2018. The growth of China’s EV market
outpaced the deployment of EV charging points in the country during the
year, highlighting the urgency of installing charging networks.
China’s
State Grid announced a goal to install some 120,000 public chargers
nationwide by 2020, and private entities including German automaker VW
also plan to roll out fast-charging networks in China to support EV
sales.
In Europe, Shell stepped into the EV industry with the
installation of 80 ultra-fast, 350 kW charging points in western Europe,
which can add some 150 kilometres of vehicle range in 5 minutes, or
fully charge an EV battery in 10 minutes.
In the Netherlands, the energy storage company Leclanché is piloting the use of stationary energy storage in EV fast-charging networks, and as of early 2018 an initial 60 charging points that provide charge times of around 20 minutes had been installed.